Python dictionaries are another collection. Real word dictionaries are a good analogy to understand them: they contain a list of items, each item has a key and a value.
In the traditional dictionary, the key is the word and the value is the explanation or description of it. In Python you can do something similar.
Related course: Complete Python Programming Course & Exercises
Example
Introduction
In a more strict way of speaking (mathematical), a dictionary is a one-to-one mapping. For every key in the dictionary there is a value. This value is assigned to the key.
dictionary: a set which contains (key, value) pairs
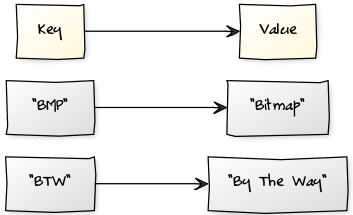
For every key in a dictionary, there is a value. Unlike lists, dictionaries do not have an specific order.
That means if you were to define a dictionary and loop over it, each time the output could be different because Python neglects the order.
Defintion
Lets type some code! You can create a dictionary with a one liner. A dictionary is defined with these brackets {}.
1 |
words = {} |
Beware: This is just two characters different from a list. Making a typo here, would mix it up with a list.
Then you can create a mapping. A mapping is defined as a key,value pair. First define
the key then the value:
1
words[key] = value
You can use strings as keys. A key defintion could be :
words['PRONTO']
Dictionary example
In the example below we define some key,value pairs and then print them using their
unique keys.
Type the code below, save it and run it:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#!/usr/bin/python
words = {}
words["BMP"] = "Bitmap"
words["BTW"] = "By The Way"
words["BRB"] = "Be Right Back"
print words["BMP"]
print words["BRB"]
If you are a beginner, then I highly recommend this YouTube Python Playlist.
Exercise
- Make a mapping from countries to country short codes
- Print each item (key and value)