A frame in Tk lets you organize and group widgets. It works like a container. Its a rectangular area in which widges can be placed.
If you make a GUI app, you'll be using different widgets. Those widgets need to be organized somehow, that's where a frame comes in.
Related course: Python Desktop Apps with Tkinter
tkinter frame button
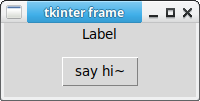
The tkinter program below demonstrates the use of a frame. It includes a button with a callback function. A frame can have padding.
1 |
from tkinter import * |
tkinter frame photo
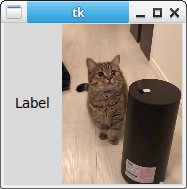
Different types of widgets can be added. The example has a tkinter frame photo. It also has a label. You can add any kind of widget to your frame.
1 |
from tkinter import * |
tkinter frame
The tkinter program below adds sevearl frames of a different color. They all have the same width and height. In other words, you can change the style of the frame.
1 |
from tkinter import * |
